Please read the features overview to get some introductory information before using SQLSchema.

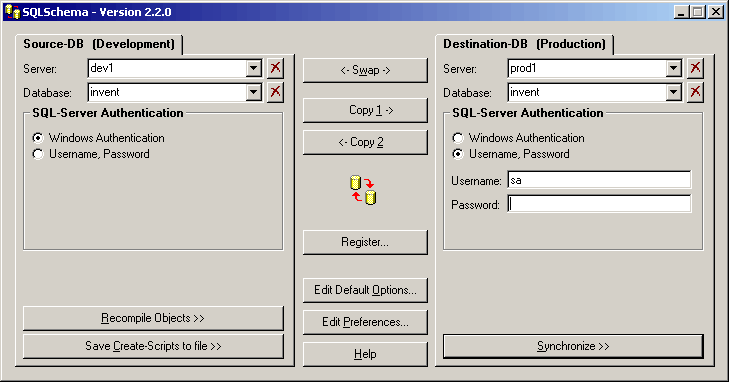
Server: |
The name of the server where the Source DB is stored. For SQL Server 2000 with more than one default instance, use the format servername\instance |
Database: |
The name of the database on the server that is used as the source for the schema comparison or data transfer. |
SQL Server Authentication: |
You can use either Windows Authentication - your current Windows credentials
are used to connect to the source DB - or SQL Server Authentication with a valid
SQL Server username and password. Note that the user must have sufficient rights to read the schema information (sys% tables and views). |
Enter server, database and login information for the destination of the schema comparison or data transfer. The user used to log into the destination DB must have enough rights to create and alter tables, views, etc. Generally speaking, the user has to be dbo in the destination DB for SQLSchema to execute correctly.
Swap, Copy |
Swap or copy the login information between source and destination panes. |
Register |
Register your copy of SQL Schema. After registration, this button will not be available any more. |
Edit Default Options |
Open the Options dialog. |
Edit Preferences |
Open the Preferences dialog. |
Help |
Opens this help text. |
Recompile Objects |
Re-creates all views, stored procedures, triggers, and functions. (Functions are
only available in SQL Server 2000 or higher) Re-creation is necessary if a view etc. is renamed in Enterprise Manager, as the name change is not updated in the object's CREATE and ALTER statements. Further, re-creation is also a check whether the definition of views, procedures, etc. is still consistent and dependencies can be resolved. |
Save Create Scripts |
Generates an SQL script file containing all CREATE statements of all objects in the source database. |
Synchronize |
Starts the schema comparison. |